How to fix vertigo sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Vertigo, a debilitating condition characterized by dizziness and loss of balance, affects millions worldwide.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the causes, diagnosis, treatment, and management of vertigo, empowering individuals to regain control over their well-being.
Delving into the complexities of vertigo, we explore its various types, including peripheral vertigo, central vertigo, and positional vertigo. Understanding the underlying causes, such as vestibular disorders, neurological conditions, and cardiovascular issues, is crucial for effective treatment.
Vertigo Overview
Vertigo is a condition that causes a sensation of spinning or dizziness. It can be a symptom of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including ear problems, neurological disorders, and medication side effects.
There are two main types of vertigo: peripheral vertigo and central vertigo. Peripheral vertigo is caused by problems in the inner ear, while central vertigo is caused by problems in the brain or brainstem.
Symptoms of Vertigo
- A sensation of spinning or dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Balance problems
- Hearing loss
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
Types of Vertigo
- Peripheral vertigois the most common type of vertigo. It is caused by problems in the inner ear, which is responsible for balance. Peripheral vertigo can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
- Ménière’s disease
- Vestibular neuritis
- Central vertigois less common than peripheral vertigo. It is caused by problems in the brain or brainstem, which are responsible for controlling balance. Central vertigo can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain tumors
Causes of Vertigo
Vertigo, a sensation of dizziness or spinning, can arise from various underlying medical conditions. These causes fall into three primary categories: vestibular disorders, neurological conditions, and cardiovascular issues.
Vestibular disorders, which affect the inner ear and its delicate balance system, are a common cause of vertigo. These disorders can range from benign conditions like benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) to more severe conditions like Ménière’s disease.
If you’re experiencing vertigo, there are a few things you can do to help fix it. First, try to identify what’s causing your vertigo. Once you know the cause, you can start to take steps to fix it. For example, if your vertigo is caused by dehydration, you can try drinking more fluids.
If your vertigo is caused by an underlying medical condition, you’ll need to see a doctor to get treatment. In the meantime, there are a few things you can do to help relieve your symptoms, such as taking over-the-counter medications or trying natural remedies . If your vertigo is severe, you may need to see a doctor for treatment.
Neurological Conditions
Neurological conditions that affect the brain or nervous system can also trigger vertigo. These conditions include migraines, strokes, and multiple sclerosis. In such cases, vertigo may be accompanied by other neurological symptoms such as headache, weakness, or numbness.
Cardiovascular Issues
Cardiovascular issues, such as low blood pressure or heart rhythm disturbances, can also cause vertigo. These conditions can lead to insufficient blood flow to the brain, resulting in dizziness or lightheadedness.
Diagnosis and Treatment
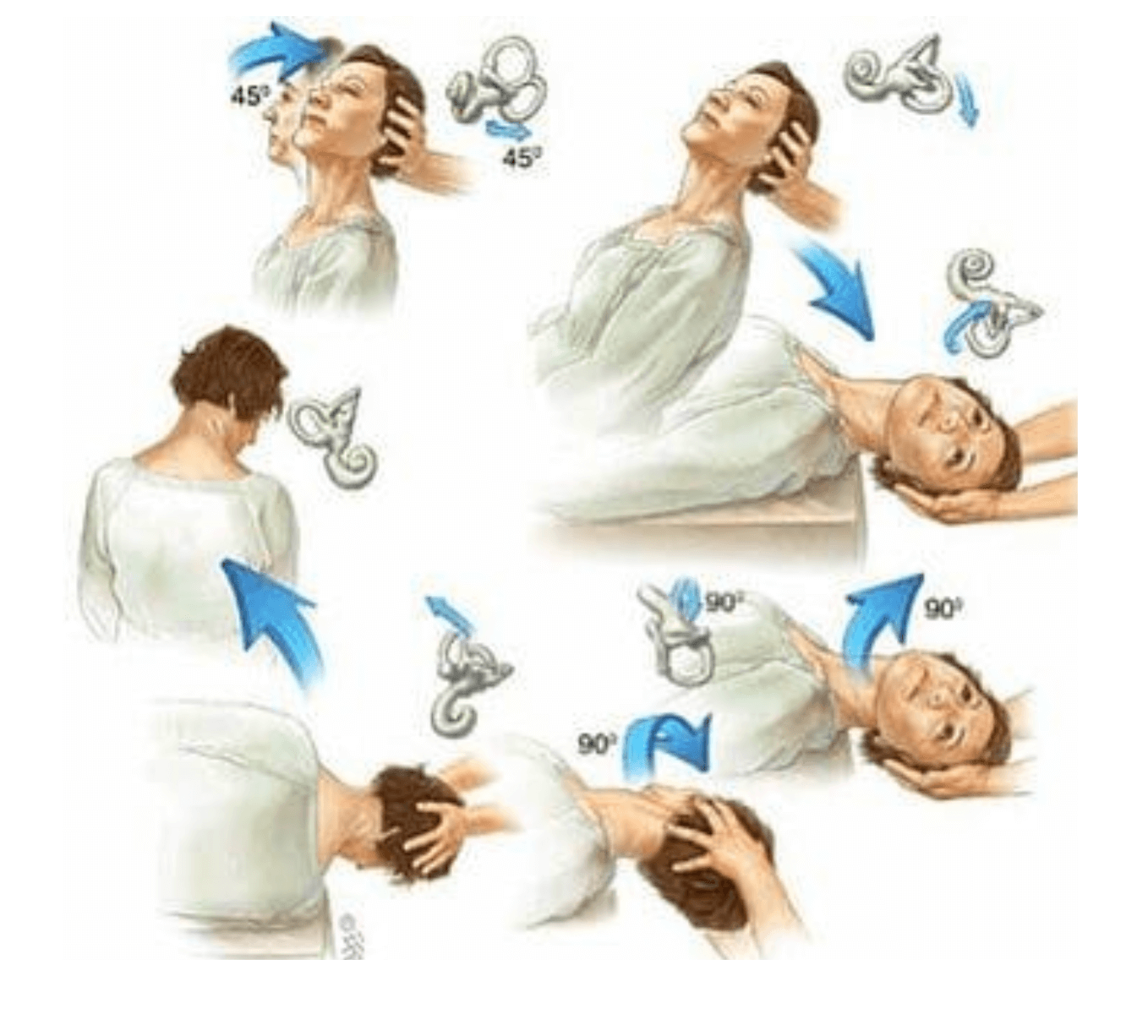
Diagnosing vertigo involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and specific tests to determine the underlying cause. A detailed account of the patient’s symptoms, including the type, duration, and any associated symptoms, is crucial.
Treatment for vertigo depends on the underlying cause. It may include:
Medications
Medications can help reduce symptoms of vertigo, such as nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Antihistamines (e.g., meclizine, dimenhydrinate)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam, lorazepam)
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy involves specific exercises designed to improve balance and coordination, reduce dizziness, and strengthen the muscles that control eye movements. Common exercises include:
- Balance exercises (e.g., standing on one leg, walking heel-to-toe)
- Vestibular exercises (e.g., head rolls, eye exercises)
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle modifications can help manage vertigo, such as:
- Avoiding sudden head movements
- Getting enough sleep
- Reducing stress
Prevention and Management

Vertigo episodes can be distressing and disruptive. Implementing preventive measures and managing symptoms effectively can improve quality of life. This section Artikels strategies for preventing vertigo and techniques for managing its symptoms.
Prevention
While not all vertigo episodes can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Manage underlying conditions:Treating underlying conditions such as ear infections, Meniere’s disease, or cervical spine issues can help prevent vertigo episodes.
- Avoid triggers:Identifying and avoiding triggers that cause vertigo, such as sudden head movements, certain medications, or dehydration, can help reduce episodes.
- Balance exercises:Performing exercises that improve balance, such as the Epley maneuver or vestibular rehabilitation therapy, can help strengthen the vestibular system and reduce vertigo symptoms.
Management
When vertigo occurs, managing symptoms effectively can help alleviate discomfort and improve functionality:
- Vestibular rehabilitation therapy:This therapy involves exercises that retrain the brain and vestibular system to compensate for balance issues.
- Medications:Medications such as anti-nausea drugs, anti-vertigo medications, or sedatives can help reduce symptoms.
- Lifestyle modifications:Restricting certain activities, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and getting adequate sleep can help manage vertigo.
Case Studies and Examples

Vertigo affects individuals in various ways, with symptoms and outcomes differing depending on the underlying cause. Here are real-life examples of individuals who have experienced vertigo, highlighting their symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment experiences:
Case 1: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), How to fix vertigo
Ben is a 55-year-old man who experienced sudden episodes of vertigo lasting a few seconds to minutes. The attacks were triggered by specific head movements, such as lying down or rolling over in bed. After consulting an otolaryngologist, Ben was diagnosed with BPPV.
He underwent a series of repositioning maneuvers, which involved moving his head into specific positions to dislodge the displaced crystals in his inner ear. After several sessions, Ben’s symptoms resolved, and he has been vertigo-free for over a year.
Case 2: Meniere’s Disease
Sarah is a 30-year-old woman who suffered from recurrent episodes of vertigo, accompanied by hearing loss and tinnitus in one ear. The attacks could last for several hours, causing severe nausea and vomiting. After extensive testing, including an audiogram and MRI scan, Sarah was diagnosed with Meniere’s disease.
She was prescribed a low-sodium diet, diuretics, and anti-nausea medication. While her symptoms have not completely disappeared, the treatment has significantly reduced the frequency and severity of her vertigo attacks.
Case 3: Vestibular Neuritis
John is a 45-year-old man who experienced sudden onset of vertigo, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. He also had difficulty walking and balancing. After visiting an emergency room, John was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis, a viral infection of the vestibular nerve.
He was prescribed antiviral medication and instructed to rest. Over the next few weeks, John’s symptoms gradually subsided, and he was able to resume his normal activities with no lingering effects.
Final Wrap-Up: How To Fix Vertigo
Managing vertigo effectively requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and self-care techniques. Medications, physical therapy, and vestibular rehabilitation can alleviate symptoms and improve balance. Embracing healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction, can further enhance recovery.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can regain control over their lives, reducing the impact of vertigo and reclaiming their sense of well-being.
