What causes vertigo dizziness – Delving into the enigmatic realm of vertigo dizziness, this comprehensive guide unveils the underlying causes and complexities of this debilitating condition, empowering you with knowledge and strategies to reclaim your equilibrium.
What is Vertigo Dizziness?
Vertigo dizziness is a common condition that causes a feeling of spinning or dizziness. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including inner ear problems, neurological disorders, and certain medications.
The symptoms of vertigo dizziness can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- A sensation of spinning or dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Balance problems
- Blurred vision
- Headaches
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
Causes of Vertigo Dizziness
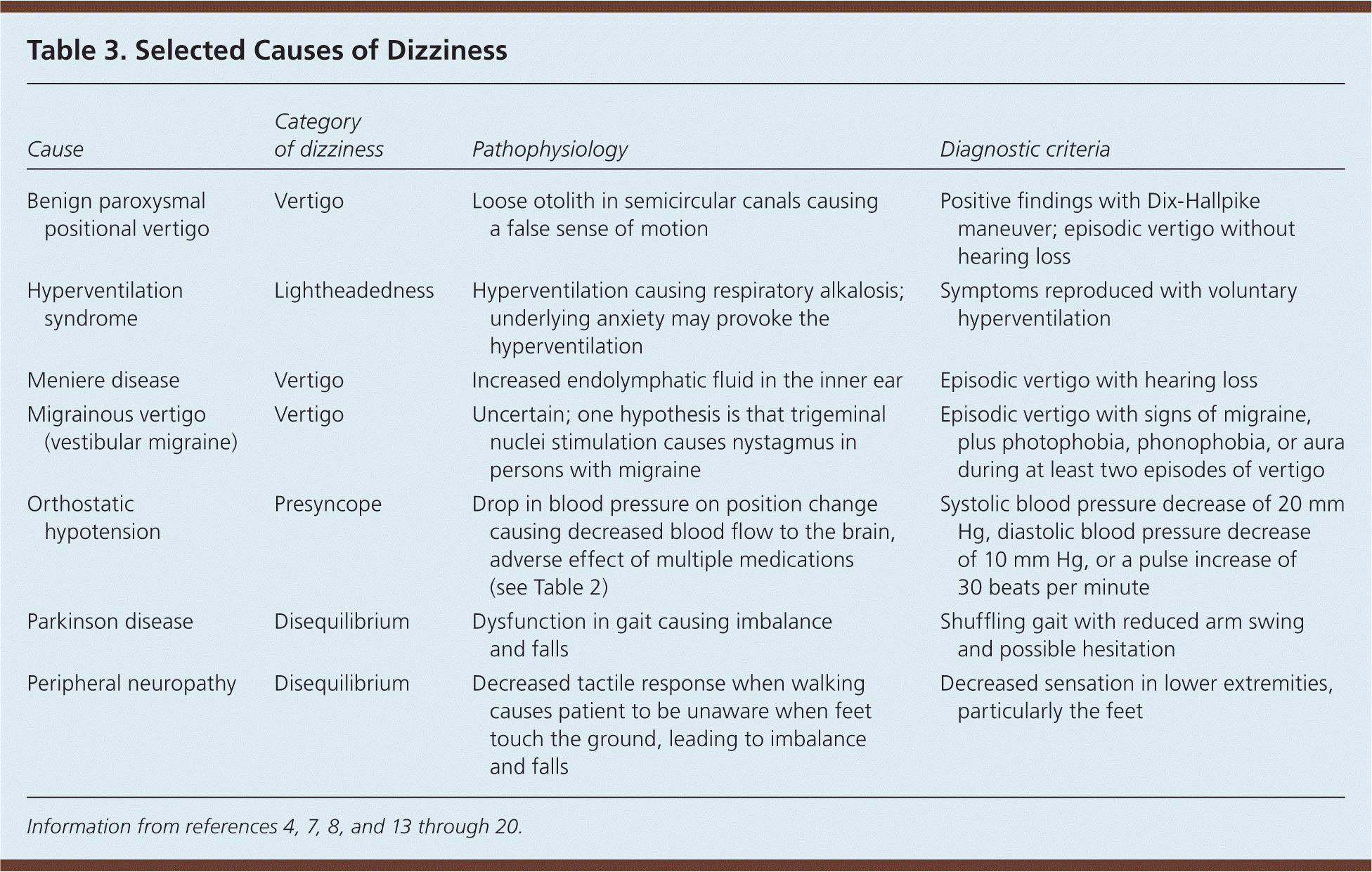
The most common cause of vertigo dizziness is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). BPPV is a condition in which tiny crystals in the inner ear become dislodged and move into the wrong part of the ear. This can cause a feeling of spinning or dizziness when the head is moved in certain positions.
Other causes of vertigo dizziness include:
- Meniere’s disease
- Vestibular neuritis
- Acoustic neuroma
- Multiple sclerosis
- Certain medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen
Causes of Vertigo Dizziness
Vertigo dizziness is a common symptom that can have various underlying causes. Understanding the potential causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective treatment.
The inner ear plays a vital role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation. When there is a disruption in the inner ear function, it can lead to vertigo dizziness.
Medical Conditions
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV):A condition where small crystals in the inner ear become dislodged, causing dizziness when the head is moved in certain positions.
- Meniere’s Disease:A disorder of the inner ear that causes episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
- Vestibular Neuritis:An inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which connects the inner ear to the brain, resulting in sudden-onset vertigo.
- Migraines:Some individuals experience vertigo as a symptom of migraine headaches.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS):A neurological condition that can affect the brain and spinal cord, sometimes leading to vertigo.
Diagnosis of Vertigo Dizziness
Identifying the underlying cause of vertigo dizziness is crucial for appropriate treatment. The diagnostic process involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests.
A thorough medical history helps identify potential risk factors, such as head injuries, medications, or underlying medical conditions. The physical examination includes a neurological assessment, ear examination, and balance tests.
Vertigo dizziness can be caused by a variety of factors, including inner ear problems, neurological disorders, and certain medications. In some cases, vertigo can be a symptom of an acute vertigo attack , which is a sudden, severe episode of dizziness that can last for several hours or even days.
While acute vertigo attacks can be frightening, they are usually not a sign of a serious medical condition and will resolve on their own. However, if you experience frequent or severe vertigo, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Diagnostic Tests
Various diagnostic tests can aid in pinpointing the cause of vertigo dizziness:
- Videonystagmography (VNG):Records eye movements to assess the function of the vestibular system and detect nystagmus (involuntary eye movements).
- Electronystagmography (ENG):Similar to VNG, but uses electrodes to measure electrical signals in the eyes.
- Rotary chair test:Rotates the patient in a chair while recording eye movements and assessing balance.
- Caloric stimulation test:Involves irrigating the ear canal with warm and cold water to stimulate the vestibular system.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan:May be used to rule out structural abnormalities in the brain or inner ear.
Treatment of Vertigo Dizziness
Managing vertigo dizziness requires a multifaceted approach, considering the underlying cause and individual needs. Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, aiming to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Medications
Medications can provide symptomatic relief by reducing nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Anti-nausea medications: Prochlorperazine, meclizine, dimenhydrinate
- Anti-vertigo medications: Betahistine, cinnarizine
- Vestibular suppressants: Diazepam, lorazepam
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy exercises, known as vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT), focus on improving balance and reducing dizziness. VRT involves specific head and body movements designed to:
- Enhance balance and coordination
- Strengthen the vestibular system
- Rehabilitate the brain’s ability to process sensory information
Lifestyle Changes, What causes vertigo dizziness
Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact vertigo dizziness management. Simple yet effective measures include:
- Avoiding sudden head movements
- Limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption
- Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine
- Reducing stress and anxiety
Prevention of Vertigo Dizziness: What Causes Vertigo Dizziness
Vertigo dizziness can be a debilitating condition that can significantly impact your quality of life. While some cases of vertigo dizziness are caused by underlying medical conditions that require specific treatment, many cases can be prevented by making lifestyle changes that reduce your risk factors.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Age:The risk of vertigo dizziness increases with age, especially in people over 65.
- Gender:Women are more likely to experience vertigo dizziness than men.
- Obesity:Being overweight or obese increases your risk of developing vertigo dizziness.
- Smoking:Smoking damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, which can lead to vertigo dizziness.
- Alcohol consumption:Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the inner ear and increase your risk of vertigo dizziness.
- Certain medications:Some medications, such as antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants, can cause vertigo dizziness as a side effect.
Lifestyle Changes, What causes vertigo dizziness
There are several lifestyle changes you can make to help prevent vertigo dizziness:
- Maintain a healthy weight:If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help reduce your risk of developing vertigo dizziness.
- Quit smoking:Smoking damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, which can lead to vertigo dizziness. Quitting smoking can help reduce your risk of developing this condition.
- Limit alcohol consumption:Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the inner ear and increase your risk of vertigo dizziness. Limiting your alcohol intake can help reduce your risk of developing this condition.
- Be cautious with medications:If you are taking any medications that can cause vertigo dizziness as a side effect, talk to your doctor about other options.
- Get regular exercise:Regular exercise can help improve your balance and coordination, which can help reduce your risk of falling and developing vertigo dizziness.
- Avoid sudden head movements:Sudden head movements can trigger vertigo dizziness. Try to avoid these movements as much as possible.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can help reduce your risk of developing vertigo dizziness and improve your overall health and well-being.
Final Review

In the realm of vertigo dizziness, understanding its causes is the first step towards regaining balance and well-being. Through a thorough exploration of its origins, this guide has illuminated the path to effective diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
